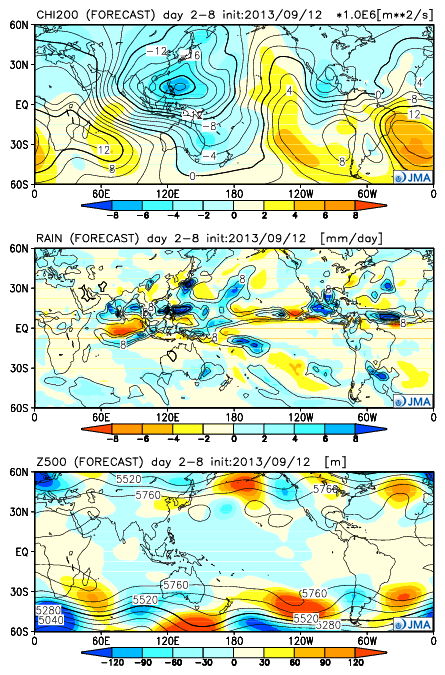
-
توجه: در صورتی که از کاربران قدیمی ایران انجمن هستید و امکان ورود به سایت را ندارید، میتوانید با آیدی altin_admin@ در تلگرام تماس حاصل نمایید.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
مباحث عمومی هواشناسی
- شروع کننده موضوع Amir Mohsen
- تاریخ شروع
- وضعیت
- موضوع بسته شده است.
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
سلام
به دوست عزیز تازه واردمون هم خوش آمد میگم و امیدوارم در کنار هم لحظات خوب و مفیدی رو در پیشرو داشته باشیم:گل:
به دوست عزیز تازه واردمون هم خوش آمد میگم و امیدوارم در کنار هم لحظات خوب و مفیدی رو در پیشرو داشته باشیم:گل:
سلام دوستان
من امروز عضو شدم. ببخشین تو بهار عضو شدم ولی این اولین پستمه.

mahmood600
کاربر ويژه
شهاب از بوشهر
کاربر ويژه
سلام دوستان.
دلم براتون تنگ شده بود.
گفتم عرض ارادتی داشته باشم هر چند که میدونم بودن من در اینجا شما رو ناراحت میکنه.
شرمنده ام دوستان.
دلم براتون تنگ شده بود.
گفتم عرض ارادتی داشته باشم هر چند که میدونم بودن من در اینجا شما رو ناراحت میکنه.
شرمنده ام دوستان.
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
جا داره یک تشکر ویژه از دوستان بسیار خوب ، عالم و فهمیم اصفهانی خودم داشته باشم که همواره فعالیت مفید و بدون حاشیه ای در همه انجمن های هواشناسی داشته و دارند.:گل:
http://www.nigs.ir/Fa/publish/Doc/14/8914234.pdf
اين مقاله نقش بلاكينگ در اروپا بر ساختار و ويژگي هاي چرخندهاي مديترانه اي بررسي مي شود. براي اين منظور، با بررسي نقشه هاي همديدي فشار سطح زمين و ارتفاع ژئوپتانسيلي سطوح مياني جو در سال هاي اخير، يك چرخند مديترانه اي در حضور بلاكينگ كه در زمستان به وقوع پيوسته است، انتخاب گرديد. براي مطالعه اثر بلاكينگ بر ويژگي هاي اين چرخند، مدل ميان مقياس MM5 در دو حالت اجرا شد. 1) داده هاي GFS به عنوان ورودي مدل بكار گرفته شد و 2) با ايجاد تغييرات در ارتفاع ژئوپتانسيلي، دما و باد سطحي داده هايGFS ، در محل پشتۀ بلاكينگ، چرخند همراه بلاكينگ از نظر ساختاري به يك چرخند بدون بلاكينگ تبديل شد. پارامترهاي فيزيكي، ديناميكي و ترموديناميكي حاصل از اجراي مدل در دو حالت بررسي و مقايسه شد. نتايج نشان داد كه بلاكينگ باعث تغيير مسير چرخند به سمت عرض هاي پايين تر، ايجاد ناهنجاري منفي (مثبت) در مؤلفۀ مداري (نصف النهاري) باد، تقويت حركات قائم و تاوايي نسبي و پتانسيلي، افزايش مقدار رطوبت و بارش و به طور كلي ايجاد چرخندهاي قوي تر مي شود.
اين مقاله نقش بلاكينگ در اروپا بر ساختار و ويژگي هاي چرخندهاي مديترانه اي بررسي مي شود. براي اين منظور، با بررسي نقشه هاي همديدي فشار سطح زمين و ارتفاع ژئوپتانسيلي سطوح مياني جو در سال هاي اخير، يك چرخند مديترانه اي در حضور بلاكينگ كه در زمستان به وقوع پيوسته است، انتخاب گرديد. براي مطالعه اثر بلاكينگ بر ويژگي هاي اين چرخند، مدل ميان مقياس MM5 در دو حالت اجرا شد. 1) داده هاي GFS به عنوان ورودي مدل بكار گرفته شد و 2) با ايجاد تغييرات در ارتفاع ژئوپتانسيلي، دما و باد سطحي داده هايGFS ، در محل پشتۀ بلاكينگ، چرخند همراه بلاكينگ از نظر ساختاري به يك چرخند بدون بلاكينگ تبديل شد. پارامترهاي فيزيكي، ديناميكي و ترموديناميكي حاصل از اجراي مدل در دو حالت بررسي و مقايسه شد. نتايج نشان داد كه بلاكينگ باعث تغيير مسير چرخند به سمت عرض هاي پايين تر، ايجاد ناهنجاري منفي (مثبت) در مؤلفۀ مداري (نصف النهاري) باد، تقويت حركات قائم و تاوايي نسبي و پتانسيلي، افزايش مقدار رطوبت و بارش و به طور كلي ايجاد چرخندهاي قوي تر مي شود.
جا داره یک تشکر ویژه از دوستان بسیار خوب ، عالم و فهمیم اصفهانی خودم داشته باشم که همواره فعالیت مفید و بدون حاشیه ای در همه انجمن های هواشناسی داشته و دارند.:گل:
اميرمحسن جان شما لطف داريد
هزاران بسته گز مخصوص تقديم شما:گل:
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
برترین تصاویر روز دنیا تقدیم به دوستان خوب و عزیزم:








Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
Whale of a Surprise: Humpbacks Winter in Antarctica
Elizabeth Howell, LiveScience Contributor | September 16, 2013 10:40am ET

Underwater conversations between humpbacks have revealed a surprising secret: Some of the whales in the Southern Hemisphere appear to skip their northward migration and stay in frigid Antarctic waters for the winter.
Elizabeth Howell, LiveScience Contributor | September 16, 2013 10:40am ET
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
Meteorite Minerals Hint at Earth Extinctions, Climate Change
by Jeremy Hsu, Astrobiology Magazine | September 16, 2013 10:23am ET

A huge asteroid that wiped out the dinosaurs may not have been the only cosmic event to cause mass extinctions or change Earth’s climate. Tiny minerals leftover from many smaller meteorites could provide the geological evidence needed to show how rocks falling from the sky changed the course of life’s evolution on our planet more than just once.
The tiny minerals called spinels — about the size of a sand grain — can survive the harshest weather and chemical changes on Earth’s surface. Swedish researchers hope to collect enough of the spinels in different parts of the world to connect the dots between the breakup of huge asteroids in space and certain extinction or climate events during Earth’s history.
"I think it would be very interesting if our spinel approach in the long run could provide empirical evidence for how asteroid showers in the inner solar system correlate with the onset of ice ages," Birger Schmitz, a marine geologist at Lund University in Sweden, said. [Potentially Dangerous Asteroids (Images)]
The hunt for spinels has led Schmitz and his colleagues to dissolve tons of rocks in acid over the past decade or so — many of the rocks originating from a commercial limestone quarry in Thorsberg, Sweden. Such a tactic could reveal convincing patterns in the geological records that scientists cannot piece together from the occasional fossilized meteorite or rare impact crater.

Meteor Crater is one of the youngest and best-preserved impact craters on Earth. The crater formed roughly 50,000 years ago when a 30-meter-wide, iron-rich meteor weighing 100,000 tons struck the Arizona desert at an estimated 20 kilometers per second. The resulting explosion exceeded the combined force of today's nuclear arsenals and created a 1.1-kilometer-wide, 200-meter-deep crater.
Without a trace
Most meteorites that have fallen to Earth end up disappearing without becoming fossilized or leaving an impact crater for scientists to find. That has made it virtually impossible for scientists to recover enough evidence to back theories about how astronomical events have tied into Earth’s history.
"We know that in desert areas on Earth, meteorites typically decompose within 20 [thousand] to 30,000 years," Schmitz said. "In wetter areas, decomposition goes faster."
But the vanishing meteorites do leave behind different types of spinels, including extremely tough chromium or alumina oxides. The chemical and isotopic fingerprints of such spinels reveal what type of meteorites they originate from. Scientists now know that extraterrestrial spinel minerals can be found in the layers of built-up sediment of almost any age over the past 3.5 billion years.
Such spinels can reveal differences in the rate and types of meteorites falling to Earth at different times in the planet’s history, Schmitz said in the June issue of the journal Chemie der Erde. They could also reveal more about the chemical makeup of asteroids, or help scientists understand if any asteroid breakups affected life on Earth in the past.
Beyond dinosaur extinction

 A scientist working in the Meteorite Processing Laboratory at NASA Johnson Space Center.
A scientist working in the Meteorite Processing Laboratory at NASA Johnson Space Center.Credit: NASAView full size image
The spinel record could reveal more extinction events with extraterrestrial links than just the mass dinosaur extinction. An earlier mass extinction during the Frasnian-Fammenian period about 372 million years ago coincides with at least three large impact craters.
"There are many large craters on Earth associated with this event, but no close connection between one large impact and the extinction event has yet been shown," Schmitz said.
But falling space rocks may bring more than just destruction to Earth. Perhaps the greatest explosion of new ocean life in Earth’s history took place during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event about 470 million years ago — a period coinciding with the largest known asteroid breakup in the solar system’s asteroid belt over the last 3 billion years.
Schmitz and colleagues discovered a rapid increase in the number of spinels found in the limestone rock layers marking the start of that diversification period at sites in Sweden, western Russia and central China. They speculate that the asteroid breakup led to frequent impacts on Earth by kilometer-sized asteroids that could have spawned the resulting changes in the diversity of life. [Wipe Out: History's Most Mysterious Extinctions (Countdown)]

 Spinel seen in a sample from the Allende meteorite.
Spinel seen in a sample from the Allende meteorite. Credit: CalTechView full size image
Another theory links asteroid showers to Earth’s three most recent major ice ages that occurred about every 250 to 300 million years. No definitive proof exists yet, but the ice age periods roughly coincide with the sun’s orbit around the galaxy every 225 to 250 million years — an event that could expose Earth to more frequent meteorite falls at certain periods. The study of spinels could help prove such theories right or wrong in the coming years.
Lab science on acid
Building a record of Earth’s history through extraterrestrial spinels still represents a fairly new idea, despite scientists having known about spinels for several decades. But Schmitz is looking forward to continuing the hunt for spinels with a specially designed lab at Lund University.
The new lab will use acid to dissolve about 5 to 10 tons of sedimentary limestone per year in search of spinels — a big step up from how Schmitz’s group handled just over one tenth of a ton per year about 15 years ago. Industrial-grade lab equipment includes acid-resistant pumps for injecting acid into large plastic barrels holding different rock samples.
The climate throughout the Mediterranean Basin is relatively the same although temperatures in the east are warmer than those in the west. The temperature of the water at the surface has risen in recent years because of the greenhouse effect. Because the Mediterranean is a relatively small sea, it warms much faster than the larger bodies of water. Off the coasts of Israel and Egypt, the sea warms to 31° Celsius in the summer and cools to 16° Celsius in the winter. In the western portion of the Mediterranean, summer water temperature reaches 26° Celsius and in the winter drops to 11° Celsius.
The climate in the eastern Mediterranean Basin is characterized by hot, dry summers and cold, rainy winters. The summer coastal areas are extremely muggy in the summer but temperatures there are milder than inland. Winter temperatures near the coast are also milder than inland.
Two major weather systems affect the Mediterranean Basin: cold weather systems over Europe and the subtropical high over the desert areas to the south. In the summer, the subtropical high spreads northward to include southern Europe, causing hot, dry weather. This is pronounced in Israel. The subtropical high retreats in the fall allowing cold weather systems accompanied by rain to enter the Mediterranean Basin. High altitude troughs bring rain to Israel. Because of global warming, the subtropical high has strengthened. It arrives sooner in the spring and leaves later in the autumn. The result has been warmer temperatures and less precipitation throughout the Mediterranean Basin. The Mediterranean Sea is relatively small, so, when rain-bearing systems do develop they are shallower than systems over the open oceans where great storms such as hurricanes and typhoons develop. The geography of the Mediterranean doesn't allow such storms to develop. The rise in water temperature has led to a rise in surface temperature along the coasts. One degree increase in water temperature translates into a two-degree rise in air temperature. The rise in water temperature is expected to bring increased autumn rainfall to Israel's coastal areas.
آب و هوایی در سراسر حوضه مدیترانه است که نسبتا همان اگر چه درجه حرارت در شرق گرمتر از کسانی که در غرب. درجه حرارت آب در سطح در سال های اخیر به دلیل اثر گلخانه ای افزایش یافته است. از آنجا که دریای مدیترانه دریای نسبتا کوچک است، آن را گرم بسیار سریعتر نسبت به بدن بزرگتر از آب است. در سواحل اسرائیل و مصر، با گرم شدن دریا تا 31 درجه سانتیگراد در تابستان و سرد به 16 درجه سانتیگراد در زمستان. در بخش غربی از دریای مدیترانه، دمای آب در تابستان به 26 درجه سانتیگراد و در زمستان تا 11 قطره درجه سلسیوس است.
آب و هوا در شرق حوضه مدیترانه، تابستانهای گرم و خشک و زمستانهای سرد، بارانی مشخص می شود. تابستان مناطق ساحلی در تابستان بسیار گرم است اما دمای احتراق وجود دارد خفیف تر از داخلی است. درجه حرارت در زمستان در نزدیکی ساحل نیز خفیف تر از داخلی است.
دو سیستم آب و هوای بزرگ را تحت تاثیر قرار حوضه مدیترانه: سیستم های آب و هوای سرد در سراسر اروپا و بالا نیمه گرمسیری بیش از مناطق بیابانی به سمت جنوب. در تابستان، اسپرد بالا نیمه گرمسیری شمال به جنوب اروپا، باعث گرم، آب و هوای خشک. این در اسرائیل تلفظ شده است. خلوت نیمه گرمسیری در پاییز اجازه می دهد سیستم های آب و هوای سرد به همراه باران به وارد حوضه مدیترانه. فرورفتگی با ارتفاع بالا را به باران به اسرائیل. از آنجا که از گرم شدن کره زمین، بالا نیمه گرمسیری تقویت شده است. می رسد زودتر در بهار و بعد از آن برگ در پاییز. نتیجه این شده است درجه حرارت گرمتر و بارش کمتر در سراسر حوضه مدیترانه. دریای مدیترانه است که نسبتا کوچک است، بنابراین، هنگامی که سیستم تحمل باران را توسعه آنها کم عمق از سیستم در بالای سطح اقیانوسها باز که در آن طوفان بزرگ مانند طوفان و توفان توسعه. جغرافیای مدیترانه اجازه نمی دهد که چنین طوفان به توسعه. افزایش درجه حرارت آب منجر به افزایش دمای سطح در امتداد سواحل. یک درجه افزایش در ترجمه دمای آب به دو درجه افزایش در دمای هوا. انتظار می رود که افزایش درجه حرارت آب را افزایش بارش های پاییز به مناطق ساحلی اسرائیل
شما را عرض نکردم.
شما در همه حال به من لطف داشتید.
بعضی از دوستان را عرض میکنم که از من کینه به دل گرفتند.
:خنده1: افسايد شد
والله چى بگم ولى من فك ميكنم فروم ها كارى به كار هم نداشته باشند بهتره:گل:
سپاس از ترجمه متن فوق:گل::گل:
شاخص MO ، در واقع شاخص مديترانه مى باشد هرگاه NAO منفى باشد بادهاى غربى باران آور به راحتى وارد مديترانه شده و باعث سيكلون زايى مديترانه مى شوند ، بهنگام NAO منفى و مثبت بودن شاخص سيكلونزائى مديترانه ( MO ) مديترانه گرم تر از نرمال و فعال ( چرخند زا ) خواهد بود و بهنگام مثبت بودن NAO فعاليت مديترانه كم مى شود .
بهنگام منفى بودن AO و NAO شاهد فعاليت بسيار مديترانه خواهيم بود اما منفى بودن اين دو شاخص طى زمستان باعث فرارفت هواى گرم و مرطوب استوايى به سمت خاورميانه مى شود و بهنگام فاز مثبت اين دو نوسان شاهد ادغام دو پرفشار آزور و سيبرى بوده و اين باعث ريزش هواى سرد قطبى به سمت خاورميانه مى شود .
بنابراين هنگام منفى بودن NAO كشورهاى سوريه ، لبنان ، اسرائيل ، فلسطين ، تركيه ، عراق و ايران شاهد هوايى معتدل و مرطوب و هنگام مثبت بودن AO و NAO شاهد هوايي سرد و خشك خواهند بود .
طبق پيش بينى ها دو نوسان قطب شمال ( AO ) و اطلس شمالى ( NAO ) از اواخر سپتامبر شديدا منفى خواهند شد.
طى زمستان ١٣٨٨ AO شديدا منفى و طى زمستان ١٣٨٦ AO شديدا مثبت بود !
شاخص MO ، در واقع شاخص مديترانه مى باشد هرگاه NAO منفى باشد بادهاى غربى باران آور به راحتى وارد مديترانه شده و باعث سيكلون زايى مديترانه مى شوند ، بهنگام NAO منفى و مثبت بودن شاخص سيكلونزائى مديترانه ( MO ) مديترانه گرم تر از نرمال و فعال ( چرخند زا ) خواهد بود و بهنگام مثبت بودن NAO فعاليت مديترانه كم مى شود .
بهنگام منفى بودن AO و NAO شاهد فعاليت بسيار مديترانه خواهيم بود اما منفى بودن اين دو شاخص طى زمستان باعث فرارفت هواى گرم و مرطوب استوايى به سمت خاورميانه مى شود و بهنگام فاز مثبت اين دو نوسان شاهد ادغام دو پرفشار آزور و سيبرى بوده و اين باعث ريزش هواى سرد قطبى به سمت خاورميانه مى شود .
بنابراين هنگام منفى بودن NAO كشورهاى سوريه ، لبنان ، اسرائيل ، فلسطين ، تركيه ، عراق و ايران شاهد هوايى معتدل و مرطوب و هنگام مثبت بودن AO و NAO شاهد هوايي سرد و خشك خواهند بود .
طبق پيش بينى ها دو نوسان قطب شمال ( AO ) و اطلس شمالى ( NAO ) از اواخر سپتامبر شديدا منفى خواهند شد.
طى زمستان ١٣٨٨ AO شديدا منفى و طى زمستان ١٣٨٦ AO شديدا مثبت بود !
سپاس از ترجمه متن فوق:گل::گل:
شاخص MO ، در واقع شاخص مديترانه مى باشد هرگاه NAO منفى باشد بادهاى غربى باران آور به راحتى وارد مديترانه شده و باعث سيكلون زايى مديترانه مى شوند ، بهنگام NAO منفى و مثبت بودن شاخص سيكلونزائى مديترانه ( MO ) مديترانه گرم تر از نرمال و فعال ( چرخند زا ) خواهد بود و بهنگام مثبت بودن NAO فعاليت مديترانه كم مى شود .
بهنگام منفى بودن AO و NAO شاهد فعاليت بسيار مديترانه خواهيم بود اما منفى بودن اين دو شاخص طى زمستان باعث فرارفت هواى گرم و مرطوب استوايى به سمت خاورميانه مى شود و بهنگام فاز مثبت اين دو نوسان شاهد ادغام دو پرفشار آزور و سيبرى بوده و اين باعث ريزش هواى سرد قطبى به سمت خاورميانه مى شود .
بنابراين هنگام منفى بودن NAO كشورهاى سوريه ، لبنان ، اسرائيل ، فلسطين ، تركيه ، عراق و ايران شاهد هوايى معتدل و مرطوب و هنگام مثبت بودن AO و NAO شاهد هوايي سرد و خشك خواهند بود .
طبق پيش بينى ها دو نوسان قطب شمال ( AO ) و اطلس شمالى ( NAO ) از اواخر سپتامبر شديدا منفى خواهند شد.
طى زمستان ١٣٨٨ AO شديدا منفى و طى زمستان ١٣٨٦ AO شديدا مثبت بود !
ترجمش کسی کرده که تازه زبان خارجه یادگرفته:خجالت:
آب و هوایی در سراسر حوضه مدیترانه است که نسبتا همان اگر چه درجه حرارت در شرق گرمتر از کسانی که در غرب. درجه حرارت آب در سطح در سال های اخیر به دلیل اثر گلخانه ای افزایش یافته است. از آنجا که دریای مدیترانه دریای نسبتا کوچک است، آن را گرم بسیار سریعتر نسبت به بدن بزرگتر از آب است. در سواحل اسرائیل و مصر، با گرم شدن دریا تا 31 درجه سانتیگراد در تابستان و سرد به 16 درجه سانتیگراد در زمستان. در بخش غربی از دریای مدیترانه، دمای آب در تابستان به 26 درجه سانتیگراد و در زمستان تا 11 قطره درجه سلسیوس است.
آب و هوا در شرق حوضه مدیترانه، تابستانهای گرم و خشک و زمستانهای سرد، بارانی مشخص می شود. تابستان مناطق ساحلی در تابستان بسیار گرم است اما دمای احتراق وجود دارد خفیف تر از داخلی است. درجه حرارت در زمستان در نزدیکی ساحل نیز خفیف تر از داخلی است.
دو سیستم آب و هوای بزرگ را تحت تاثیر قرار حوضه مدیترانه: سیستم های آب و هوای سرد در سراسر اروپا و بالا نیمه گرمسیری بیش از مناطق بیابانی به سمت جنوب. در تابستان، اسپرد بالا نیمه گرمسیری شمال به جنوب اروپا، باعث گرم، آب و هوای خشک. این در اسرائیل تلفظ شده است. خلوت نیمه گرمسیری در پاییز اجازه می دهد سیستم های آب و هوای سرد به همراه باران به وارد حوضه مدیترانه. فرورفتگی با ارتفاع بالا را به باران به اسرائیل. از آنجا که از گرم شدن کره زمین، بالا نیمه گرمسیری تقویت شده است. می رسد زودتر در بهار و بعد از آن برگ در پاییز. نتیجه این شده است درجه حرارت گرمتر و بارش کمتر در سراسر حوضه مدیترانه. دریای مدیترانه است که نسبتا کوچک است، بنابراین، هنگامی که سیستم تحمل باران را توسعه آنها کم عمق از سیستم در بالای سطح اقیانوسها باز که در آن طوفان بزرگ مانند طوفان و توفان توسعه. جغرافیای مدیترانه اجازه نمی دهد که چنین طوفان به توسعه. افزایش درجه حرارت آب منجر به افزایش دمای سطح در امتداد سواحل. یک درجه افزایش در ترجمه دمای آب به دو درجه افزایش در دمای هوا. انتظار می رود که افزایش درجه حرارت آب را افزایش بارش های پاییز به مناطق ساحلی اسرائیل
ترجمهٔ جناب google translator هست! بدون ویرایش متن
ترجمهٔ جناب google translator هست! بدون ویرایش متن
همين كه محبت داشت ترجمه كرد و گذاشت فروم دستش درد نكنه
مقاله ميگه مديترانه دماش روى سيكلونزائى ش خيلى تاثير داره
ترجمهٔ جناب google translator هست! بدون ویرایش متن
نه خیرم اشتباه کردی دکتر جان اونی شما فکر میکنی نیست من تافل کانون زبانو دارم بلامیسر ادونسو هم خوندم ولی اینو ترجمه نکردم کار یکی دیگه بود
نه خیرم اشتباه کردی دکتر جان اونی شما فکر میکنی نیست من تافل کانون زبانو دارم بلامیسر ادونسو هم خوندم ولی اینو ترجمه نکردم کار یکی دیگه بود
+ اینکه ردم شدما چون که استادا ه من زیاد لطف داشتن بخاظره تیکه های که سر جلسات میداختم فضا عوض میشد!
شب عالی
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
[h=2]The state of climate science: ‘fluxed up’ Posted on September 15, 2013 by Anthony Watts
Science not settled, still in a state of flux – IPCC AR5 in disarray. It is looking like my single word quote in Rolling Stone “stillborn”, will be accurate.
The title is my twist on what Dr. Judith Curry said in an email to David Rose in his latest article about the upcoming IPCC AR5 report:

BTW, Rose is Jewish.
And finally, he calls out Bob Ward, but unfortunately doesn’t mention his past as a punk rocker before he became a climate activist:
[h=3]‘A REFLECTION OF EVIDENCE FROM NEW STUDIES’… THE IPCC CHANGES ITS STORY What they say: ‘The rate of warming since 1951 [has been] 0.12C per decade.’
What this means: In their last hugely influential report in 2007, the IPCC claimed the world was warming at 0.2C per decade. Here they admit there has been a massive cut in the speed of global warming – although it’s buried in a section on the recent warming ‘pause’. The true figure, it now turns out, is not only just over half what they thought – it’s below their lowest previous estimate.
What they say: ‘Surface temperature reconstructions show multi-decadal intervals during the Medieval Climate Anomaly (950-1250) that were in some regions as warm as in the late 20th Century.’
What this means: As recently as October 2012, in an earlier draft of this report, the IPCC was adamant that the world is warmer than at any time for at least 1,300 years. Their new inclusion of the ‘Medieval Warm Period’ – long before the Industrial Revolution and its associated fossil fuel burning – is a concession that its earlier statement is highly questionable.
What they say: ‘Models do not generally reproduce the observed reduction in surface warming trend over the last 10 – 15 years.’
What this means: The ‘models’ are computer forecasts, which the IPCC admits failed to ‘see… a reduction in the warming trend’. In fact, there has been no statistically significant warming at all for almost 17 years – as first reported by this newspaper last October, when the Met Office tried to deny this ‘pause’ existed.In its 2012 draft, the IPCC didn’t mention it either. Now it not only accepts it is real, it admits that its climate models totally failed to predict it.
What they say: ‘There is medium confidence that this difference between models and observations is to a substantial degree caused by unpredictable climate variability, with possible contributions from inadequacies in the solar, volcanic, and aerosol forcings used by the models and, in some models, from too strong a response to increasing greenhouse-gas forcing.’
What this means: The IPCC knows the pause is real, but has no idea what is causing it. It could be natural climate variability, the sun, volcanoes – and crucially, that the computers have been allowed to give too much weight to the effect carbon dioxide emissions (greenhouse gases) have on temperature change.
What they say: ‘Climate models now include more cloud and aerosol processes, but there remains low confidence in the representation and quantification of these processes in models.’
What this means: Its models don’t accurately forecast the impact of fundamental aspects of the atmosphere – clouds, smoke and dust.
What they say: ‘Most models simulate a small decreasing trend in Antarctic sea ice extent, in contrast to the small increasing trend in observations… There is low confidence in the scientific understanding of the small observed increase in Antarctic sea ice extent.’
What this means: The models said Antarctic ice would decrease. It’s actually increased, and the IPCC doesn’t know why.
What they say: ‘ECS is likely in the range 1.5C to 4.5C… The lower limit of the assessed likely range is thus less than the 2C in the [2007 report], reflecting the evidence from new studies.’
What this means: ECS – ‘equilibrium climate sensitivity’ – is an estimate of how much the world will warm every time carbon dioxide levels double. A high value means we’re heading for disaster. Many recent studies say that previous IPCC claims, derived from the computer models, have been way too high. It looks as if they’re starting to take notice, and so are scaling down their estimate for the first time.
Rose also mentions the new paper from Nic Lewis taking the Met office climate model to task for having an ECS of 4.6C, which is greater than even the IPCC is claiming:
Lewis’s paper is scathing about the ‘future warming’ document issued by the Met Office in July, which purported to explain why the current 16-year global warming ‘pause’ is unimportant, and does not mean the ECS is lower than previously thought.
Lewis says the document made misleading claims about other scientists’ work – for example, misrepresenting important details of a study by a team that included Lewis and 14 other IPCC experts. The team’s paper, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience in May, said the best estimate of the ECS was 2C or less – well under half the Met Office estimate.
He also gives evidence that another key Met Office model is inherently skewed. The result is that it will always produce high values for CO2-induced warming, no matter how its control knobs are tweaked, because its computation of the cooling effect of smoke and dust pollution – what scientists call ‘aerosol forcing’ – is simply incompatible with the real world.
This has serious implications, because the Met Office’s HadCM3 model is used to determine the Government’s climate projections, which influence policy.
Mr Lewis concludes that the Met Office modelling is ‘fundamentally unsatisfactory, because it effectively rules out from the start the possibility that both aerosol forcing and climate sensitivity are modest’. Yet this, he writes, ‘is the combination that recent observations support’.
We live in interesting times.
Read Rose’s article here: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/art...cts-greenhouse-gases-wrong.html#ixzz2exAZ99b9
Science not settled, still in a state of flux – IPCC AR5 in disarray. It is looking like my single word quote in Rolling Stone “stillborn”, will be accurate.
The title is my twist on what Dr. Judith Curry said in an email to David Rose in his latest article about the upcoming IPCC AR5 report:
Last night Professor Judith Curry, head of climate science at Georgia Institute of Technology in Atlanta, said the leaked summary showed that ‘the science is clearly not settled, and is in a state of flux’.
She goes on to say:
She said it therefore made no sense that the IPCC was claiming that its confidence in its forecasts and conclusions has increased.
For example, in the new report, the IPCC says it is ‘extremely likely’ – 95 per cent certain – that human influence caused more than half the temperature rises from 1951 to 2010, up from ‘very confident’ – 90 per cent certain – in 2007.
Prof Curry said: ‘This is incomprehensible to me’ – adding that the IPCC projections are ‘overconfident’, especially given the report’s admitted areas of doubt.
Professor Myles Allen also got in a few licks, Prof Allen said:For example, in the new report, the IPCC says it is ‘extremely likely’ – 95 per cent certain – that human influence caused more than half the temperature rises from 1951 to 2010, up from ‘very confident’ – 90 per cent certain – in 2007.
Prof Curry said: ‘This is incomprehensible to me’ – adding that the IPCC projections are ‘overconfident’, especially given the report’s admitted areas of doubt.
‘The idea of producing a document of near-biblical infallibility is a misrepresentation of how science works, and we need to look very carefully about what the IPCC does in future.’
Rose also took Dana Nuccitelli and John Abraham to task at the Guardian over ugly death threat type comments that remain about their rebuttal to his article last week, while other comments are removed for not meeting “standards”.

BTW, Rose is Jewish.
And finally, he calls out Bob Ward, but unfortunately doesn’t mention his past as a punk rocker before he became a climate activist:
Another assault was mounted by Bob Ward, spokesman for the Grantham Institute for Climate Change at the London School of Economics.
Mr Ward tweeted that the article was ‘error-strewn’.
The eminent US expert Professor Judith Curry, who unlike Mr Ward is a climate scientist with a long list of peer-reviewed publications to her name, disagreed.
On her blog Climate Etc she defended The Mail on Sunday, saying the article contained ‘good material’, and issued a tweet which challenged Mr Ward to say what these ‘errors’ were.
He has yet to reply.
As for the state of climate science, this summary by Rose of the IPCC situation is worth sharing:Mr Ward tweeted that the article was ‘error-strewn’.
The eminent US expert Professor Judith Curry, who unlike Mr Ward is a climate scientist with a long list of peer-reviewed publications to her name, disagreed.
On her blog Climate Etc she defended The Mail on Sunday, saying the article contained ‘good material’, and issued a tweet which challenged Mr Ward to say what these ‘errors’ were.
He has yet to reply.
[h=3]‘A REFLECTION OF EVIDENCE FROM NEW STUDIES’… THE IPCC CHANGES ITS STORY What they say: ‘The rate of warming since 1951 [has been] 0.12C per decade.’
What this means: In their last hugely influential report in 2007, the IPCC claimed the world was warming at 0.2C per decade. Here they admit there has been a massive cut in the speed of global warming – although it’s buried in a section on the recent warming ‘pause’. The true figure, it now turns out, is not only just over half what they thought – it’s below their lowest previous estimate.
What they say: ‘Surface temperature reconstructions show multi-decadal intervals during the Medieval Climate Anomaly (950-1250) that were in some regions as warm as in the late 20th Century.’
What this means: As recently as October 2012, in an earlier draft of this report, the IPCC was adamant that the world is warmer than at any time for at least 1,300 years. Their new inclusion of the ‘Medieval Warm Period’ – long before the Industrial Revolution and its associated fossil fuel burning – is a concession that its earlier statement is highly questionable.
What they say: ‘Models do not generally reproduce the observed reduction in surface warming trend over the last 10 – 15 years.’
What this means: The ‘models’ are computer forecasts, which the IPCC admits failed to ‘see… a reduction in the warming trend’. In fact, there has been no statistically significant warming at all for almost 17 years – as first reported by this newspaper last October, when the Met Office tried to deny this ‘pause’ existed.In its 2012 draft, the IPCC didn’t mention it either. Now it not only accepts it is real, it admits that its climate models totally failed to predict it.
What they say: ‘There is medium confidence that this difference between models and observations is to a substantial degree caused by unpredictable climate variability, with possible contributions from inadequacies in the solar, volcanic, and aerosol forcings used by the models and, in some models, from too strong a response to increasing greenhouse-gas forcing.’
What this means: The IPCC knows the pause is real, but has no idea what is causing it. It could be natural climate variability, the sun, volcanoes – and crucially, that the computers have been allowed to give too much weight to the effect carbon dioxide emissions (greenhouse gases) have on temperature change.
What they say: ‘Climate models now include more cloud and aerosol processes, but there remains low confidence in the representation and quantification of these processes in models.’
What this means: Its models don’t accurately forecast the impact of fundamental aspects of the atmosphere – clouds, smoke and dust.
What they say: ‘Most models simulate a small decreasing trend in Antarctic sea ice extent, in contrast to the small increasing trend in observations… There is low confidence in the scientific understanding of the small observed increase in Antarctic sea ice extent.’
What this means: The models said Antarctic ice would decrease. It’s actually increased, and the IPCC doesn’t know why.
What they say: ‘ECS is likely in the range 1.5C to 4.5C… The lower limit of the assessed likely range is thus less than the 2C in the [2007 report], reflecting the evidence from new studies.’
What this means: ECS – ‘equilibrium climate sensitivity’ – is an estimate of how much the world will warm every time carbon dioxide levels double. A high value means we’re heading for disaster. Many recent studies say that previous IPCC claims, derived from the computer models, have been way too high. It looks as if they’re starting to take notice, and so are scaling down their estimate for the first time.
Rose also mentions the new paper from Nic Lewis taking the Met office climate model to task for having an ECS of 4.6C, which is greater than even the IPCC is claiming:
Lewis’s paper is scathing about the ‘future warming’ document issued by the Met Office in July, which purported to explain why the current 16-year global warming ‘pause’ is unimportant, and does not mean the ECS is lower than previously thought.
Lewis says the document made misleading claims about other scientists’ work – for example, misrepresenting important details of a study by a team that included Lewis and 14 other IPCC experts. The team’s paper, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience in May, said the best estimate of the ECS was 2C or less – well under half the Met Office estimate.
He also gives evidence that another key Met Office model is inherently skewed. The result is that it will always produce high values for CO2-induced warming, no matter how its control knobs are tweaked, because its computation of the cooling effect of smoke and dust pollution – what scientists call ‘aerosol forcing’ – is simply incompatible with the real world.
This has serious implications, because the Met Office’s HadCM3 model is used to determine the Government’s climate projections, which influence policy.
Mr Lewis concludes that the Met Office modelling is ‘fundamentally unsatisfactory, because it effectively rules out from the start the possibility that both aerosol forcing and climate sensitivity are modest’. Yet this, he writes, ‘is the combination that recent observations support’.
We live in interesting times.
Read Rose’s article here: http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/art...cts-greenhouse-gases-wrong.html#ixzz2exAZ99b9
- وضعیت
- موضوع بسته شده است.