-
توجه: در صورتی که از کاربران قدیمی ایران انجمن هستید و امکان ورود به سایت را ندارید، میتوانید با آیدی altin_admin@ در تلگرام تماس حاصل نمایید.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
مباحث عمومی هواشناسی
- شروع کننده موضوع Amir Mohsen
- تاریخ شروع
- وضعیت
- موضوع بسته شده است.
اصفهان امروزم هوایی مطبوع وعالی داره والبته کمی سرد ، پوشیده از ابر و مرطوب ، یاد آذرهای دهه 70 افتادم که گاه و بیگاه بدون انتظار قبلی و غیرمنتظره هوا ابری میشد و بسته به دمای هوا یه رگبار خفیف باران ریزه یا رگبار برف اتفاق می افتاد ... یادش بخیر
امسال تا اینجا همه چی خوب داره پیش میره ...در ادامه هم ایشالا خوب خواهد بود ...
امسال تا اینجا همه چی خوب داره پیش میره ...در ادامه هم ایشالا خوب خواهد بود ...
ali.doosti
کاربر ويژه
سلامسلام دوستان
امسال پاییز در منطقه ما کاملا متفاوت بوده
تا اینجای کار تعداد روزهای آلوده کمتر بود.
رطوبت نسبی در سطح زمین در مقایسه با سالهای گذشته بسیار قابل توجه بوده.
تعداد روزهای ابری افزایش چشمگیری داشته.
مقادیر بارش راضی کننده بوده.
شیب افت دما با آهنگ ملایمی رخ داده و یا به عبارت دیگه اختلاف بین دمای بیشینه و کمینه به نسبت سالهای گذشته کمتر بوده.
رخ داد وزش بادهای شدید نرخ نزولی داشته.
وقوع بیماریهای واگیردار همچون آنفولانزا کاهش چشمگیری داشته
Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk
چه جالب اینجا هم تقریبا این جور شده...امروز بعد از 7 روز آفتاب درومد...بیماری هم اصلا شایع نشده!
سلام
چه جالب اینجا هم تقریبا این جور شده...امروز بعد از 7 روز آفتاب درومد...بیماری هم اصلا شایع نشده!
دقیقا اینجا هم بعد از مدت ها آفتاب رو دیدیم
Sent from my GT-I9500 using Tapatalk
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
بیشتر مدلها برای روزهای 21-23 دسامبر برای شهرهایی همچون تهران - اصفهان و مشهد بارش برف در نظر گرفته اند.
البته شانس برف در ماه ژانویه هم بنظر بالاست مثل این تصویر زیر که برای شهر اصفهان هست:
فقط یک موضوع : ستون دوم دمای حسی هست:

البته شانس برف در ماه ژانویه هم بنظر بالاست مثل این تصویر زیر که برای شهر اصفهان هست:
فقط یک موضوع : ستون دوم دمای حسی هست:

هوا امروز شديدا دو نفره اس:خجالت2: هواى صاف هم صفاى خودش را داره اى كاش زاينده رودآب داشت
اميدوارم در اين مدت وقفه بارشى لااقل باد بياد كه آلودگى نداشته باشيم
يه شوخى هم بكنم اميدوارم حالا كه به توافق رسيدن تحريم بارندگى را از رو ايران بردارند و بزارن ابرهاى بارشى بيان رو كشور
اميدوارم در اين مدت وقفه بارشى لااقل باد بياد كه آلودگى نداشته باشيم
يه شوخى هم بكنم اميدوارم حالا كه به توافق رسيدن تحريم بارندگى را از رو ايران بردارند و بزارن ابرهاى بارشى بيان رو كشور
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
Iran Full Year Climatology Overview CONVENTIONS: The spelling of place names and geographical features are those used by the National Imagery and Mapping Agency (NIMA). All distances are in nautical miles (NM) and kilometers (km), except for visibility, which is in statute miles and meters. Elevations are in feet above mean sea level (MSL), with a metric conversion following. Temperatures are in degrees Fahrenheit (F) and Celsius (C). Wind speeds are in knots. Cloud bases are above ground level (AGL) unless otherwise stated; tops are above mean sea level (MSL). Precipitation amounts are in inches, with a millimeter (mm) or centimeter (cm) conversion following. Precipitation values given are liquid equivalent unless stated otherwise. Standard pressure levels are expressed in millibars (mb). Time is reported either in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) (also known as Zulu or Z), or Local (L). General Weather. Iran has an arid to semiarid climate. Summers are intensely hot, except in the mountains, while the winter is cool to cold, except in the coastal lowlands. During winter, the weather pattern is constantly changing due to the frequent passage of migratory systems. During summer hot, dry, and often dusty conditions prevail. Sky Cover. The cloudiest time of the year is winter, but low ceilings are infrequent except in the mountains. Summer skies are mostly clear. Visibility. Visibility is generally good except in arid regions, where blowing dust and sandstorms cause reduced visibility. In addition, intense heating of the desert surface produces mirages and shimmers that reduce visibility to a few hundred yards along the surface. Winds. Surface winds exceed 20 knots 10 percent of the time. The shamal winds of the Persian Gulf coast and 'winds of 120 Days' of eastern Iran are well-known here. Both are strong winds that are hot, dry, and dust filled; strong gusts and dust devils are common; 50-55-knot gusts may occur. Precipitation. Precipitation falls year-round near the Caspian Sea, particularly in the west where annual amounts exceed 50 inches (1,270 mm). The interior plains of Iran get less than 5 inches (127 mm) of rainfall per average year. Throughout the remainder of Iran, most precipitation occurs in winter and spring, with the largest amounts in the mountains. The permanent snow line during winter is near 5,000 feet (1,520 meters) across most of northern Iran. Temperature. Winter temperatures along the southern coast are 55F to 62F (13C to 17C) in the morning hours and 78F (26C) in late afternoon. Temperatures in north central Iran range from 23F (-5C) in the morning to 43F (6C) in the afternoon. Winters are very cold in the mountains; these temperatures range from 15F (-9C) in the morning to 43F (6C) in the afternoon. Summer afternoon temperatures vary from 85F (29C) along the Caspian Coast to over 110F (43C) at the head of the Persian Gulf. The morning temperatures vary from 65F to 75F (18C to 24C) along the Caspian Coast and north central Iran to 78F to 82F (26C to 28C) along the southern coast. Low humidity, except along the coastal strips, helps reduce the heat stress on personnel. POINT OF CONTACT: Address questions and comments pertaining to this narrative to AFCCC/DOC5, 151 Patton Avenue, Room 120, Asheville, NC 28801-5002. Telephone: DSN 673-9007 or Commercial (828) 271-4234. E-mail DOC5@afccc.af.mil Approved for public release: distribution is unlimited June 1988
دما يكي از مهمترين عناصر موثربرآب و هوا ومحيط زيست هرمنطقه است بنابراين فرينهاي دمايي نيز از اهميت بسياري برخوردار هستند اين تحقيق با شيوه اماري و تحليلي انجام گرفته است و هدف ازا نچام اين پژوهش شناسايي سيستم هاي گردشري است كه ميتوانند باعث بروز سرمايها فرين دراستان شود تا بتوان با دانستن علت و زمان رخداد اين سرماهاي فرين از خسارت ناشي از كاهش ناگهاني دما جلوگيري نمود دراين پژوهش به منظور تحليل همديد دماهاي فرين اصفهان داده هاي مربوط به دماي حداقل روزانه ايستگاه اصفهان درطي سالهاي 1340-1387 مورد استفاده قرارگرفته است و پس از استانداردسازي داده ها و محاسبه NTD به روش شاخص فومياكي روزهايي كه داراي دماهاي حداقل بودها ند مشخص گرديد كه از بين روزهايي كه فرين سرد اتفاق افتاده بود
دي ماه 74 به عنوان سردترين دوره انتخاب گرديد سپس نقشه هاي مربوط به دماي هوا و مولفه بادمداري و بادنصف النهاري اين تاريخ درتراز 700 هكتوپاسكال درنرم افزار گردس ترسيم شده و با بررسي اين نقشه ها معلوم گرديدكه دراين تاريخ دراصفهان ازسمت غرب ايران يك فرارفت سرد اتفاق افتاده و درواقع يك فرود بسيار عميق روي ايران تشكيل شده و تاجنوب نيز كشيده شده و باعث ريزش هواي بسيارسرد عرضهاي بالا به ايران شده است.
دي ماه 74 به عنوان سردترين دوره انتخاب گرديد سپس نقشه هاي مربوط به دماي هوا و مولفه بادمداري و بادنصف النهاري اين تاريخ درتراز 700 هكتوپاسكال درنرم افزار گردس ترسيم شده و با بررسي اين نقشه ها معلوم گرديدكه دراين تاريخ دراصفهان ازسمت غرب ايران يك فرارفت سرد اتفاق افتاده و درواقع يك فرود بسيار عميق روي ايران تشكيل شده و تاجنوب نيز كشيده شده و باعث ريزش هواي بسيارسرد عرضهاي بالا به ايران شده است.
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
وضعیت فعلی شاخصها:


-----------------------




-----------------------


معاون رییس جمهوری و رییس سازمان حفاظت محیط زیست گفت: دستگاه های سنجش آلودگی هوا برای بررسی علت بروز مشکلات تنفسی در مردم اهواز ، شناسایی آلاینده های عامل و اندازه گیری آنها به شهر اهواز ارسال شدند.
به گزارش ایرنا ،هفته گذشته مردم شهر اهواز برای دومین بار در آبان ماه امسال به دلیل آلودگی شدید هوا دچار تنگی نفس و حملات آسمی شدند و عده زیادی از مردم برای مداوا به مراکز درمانی مراجعه کردند.
معصومه ابتکار امروز- شنبه - در جمع خبرنگاران یادآور شد : این دستگاه ها نسبت به تشخیص آلاینده ها بسیار حساس هستند و از راه زمینی به شهر اهواز ارسال شدند و به احتمال زیاد امروز به اهواز می رسند. تعداد این دستگاه ها در کشور محدود است و در هشت سال گذشته با وجود کاربری زیاد به هیچ وجه از آنها استفاده نشده است.
وی گفت : بروز مشکلات تنفسی مردم اهواز به احتمال زیاد به دلیل وجود آلاینده های ازون و ترکیبات گوگردی در هوای این شهر بوده است اما بررسی ها برای رسیدن به نتیجه نهایی همچنان ادامه دارد.
ابتکار خاطرنشان کرد : احتمال می رود که علاوه براین دو آلاینده ، یک آلاینده ناشناخته نیز موجب بروز و افزایش بیماری های تنفسی در شهر اهواز شده است .
وی گفت : بر اساس بررسی های متعددی که توسط کارشناسان و محققان صاحبنظر در این زمینه انجام شده است به احتمال زیاد افزایش آلاینده های ازون و ترکیبات گوگردی عامل اصلی بروز بیماری های تنفسی است زیرا نتیجه تحقیقات نشان می دهد وجود این آلاینده ها در افرادی که زمینه تنگی نفس دارند ، موجب حملات آسمی می شود.
وی خاطرنشان کرد: در سفری که حدود 2 هفته پیش به استان خوزستان داشتم شبکه ای از ایستگاه های سنجش آلودگی هوا شامل 15 ایستگاه در کل استان خوزستان و 4 ایستگاه در شهر اهواز راه اندازی شد.
ابتکار اظهارداشت:براساس اطلاعات به دست آمده از این ایستگاه ها گازهای ازون و گوگردی در این مدت در اهواز افزایش نیافته است بنابراین یا دستگاه های موجود در ایستگاه های سنجش آلودگی هوا مشکل دارند و یا این که یک آلاینده ناشناخته دیگری عامل بروز تنگی نفس در مردم شده است .
وی افزود : در اجلاس بین المللی آب و هوا مذاکرات زیادی با مسوولان کشورهای مختلف در منطقه برای کاهش میزان گرد و غبار انجام شد. همچنین از سازمان های بین المللی برای رسیدگی به وضعیت آلودگی شهر اهواز و چهار شهر غربی کشور که تحت تاثیر شدید پدیده ریزگردها هستند، قول مساعد گرفته شد.
ابتکار افزود : در دیدار با وزیر نفت کشورمان در مورد ارتقای استاندارد سوخت به سوخت یورو 4 مذاکراتی انجام شد و در این دیدار وزیر نفت قول داد با وجود تمام محدودیتی های موجود و به رغم تحریم ها که نقش عمده ای در نرسیدن به استاندارد یورو 4 داشته اند، اقدام لازم برای ارتقای استانداردهای سوخت انجام شود.
وی ابرازامیدواری کرد که خودروسازان به تعهدات خود در زمینه تولیدمحصول با استاندارد یورو 4 عمل کنند و خود را با سوخت یورو 4 هماهنگ کنند.
معاون رییس جمهوری گفت: خودرو سازان تاکنون چندین بار مهلت خود برای تولید خودور با استاندارد یورو 4 تمدید کردند اما باید این فرصت ها بازنگری شود که این امر در دستور کار سازمان محیط زیست قرار دارد.
وی تحریم ها را در کنار عوامل دیگر یکی دیگر از موانع وزارت نفت و وزارت صنعت ، معدن و تجارت برای ارایه سوخت و خودرو با استاندارد یورو 4 اعلام کرد و افزود: در اجلاس بین المللی تغییرات آب و هوا در ورشو از سران کشورها و سازمان ملل خواستیم که این تحریم های غیرقانونی را لغو کنند چرا که نقش عمده ای در تغییرات آب و هوایی دارد.
معاون رییس جمهوری یاداور شد : بنزین یورو 4 و گاز طبیعی بهترین نوع سوختی هستند که می توان از آنها استفاده کرد .سازمان بهداشت جهانی در گزارش اخیر خود اعلام کرد گازوییل در بهترین شرایط باز هم ذرات دوده ای تولید می کند که می تواند سرطان زا باشد در حالی که این شرایط برای بنزین یورو4 و گاز طبیعی صادق نیست.
وی در مورد موضع سازمان محیط زیست در اجرای طرح زوج و فرد سراسری خودروها تاکید کرد: سازمان محیط زیست به هیچ عنوان با دایمی شدن این طرح موافق نبود اما اگر سازمان هواشناسی به دستگاه هایی مجهز شود که بتواند پیش بینی های دقیق تری ارایه دهد می توان از یکی دو روز پیش از انباشت آلاینده ها و چند روز پس از آن ، این طرح را اجرا کرد.
اجلاس بین المللی تغییرات آب و هوا از 20 آبان ماه امسال به مدت 12 روز در دو سطح کارشناسی و عالی در ورشو پایتخت لهستان برگزار شد.
علاوه بر رییس سازمان محیط زیست ، معاون علمی و فناوری رییس جمهوری به همراه نمایندگانی از وزارتخانه های نفت ، نیرو ، وزارت امور خارجه و دیگر کارشناسان از کشورمان در این اجلاس حضور داشتند.
به گزارش ایرنا ،هفته گذشته مردم شهر اهواز برای دومین بار در آبان ماه امسال به دلیل آلودگی شدید هوا دچار تنگی نفس و حملات آسمی شدند و عده زیادی از مردم برای مداوا به مراکز درمانی مراجعه کردند.
معصومه ابتکار امروز- شنبه - در جمع خبرنگاران یادآور شد : این دستگاه ها نسبت به تشخیص آلاینده ها بسیار حساس هستند و از راه زمینی به شهر اهواز ارسال شدند و به احتمال زیاد امروز به اهواز می رسند. تعداد این دستگاه ها در کشور محدود است و در هشت سال گذشته با وجود کاربری زیاد به هیچ وجه از آنها استفاده نشده است.
وی گفت : بروز مشکلات تنفسی مردم اهواز به احتمال زیاد به دلیل وجود آلاینده های ازون و ترکیبات گوگردی در هوای این شهر بوده است اما بررسی ها برای رسیدن به نتیجه نهایی همچنان ادامه دارد.
ابتکار خاطرنشان کرد : احتمال می رود که علاوه براین دو آلاینده ، یک آلاینده ناشناخته نیز موجب بروز و افزایش بیماری های تنفسی در شهر اهواز شده است .
وی گفت : بر اساس بررسی های متعددی که توسط کارشناسان و محققان صاحبنظر در این زمینه انجام شده است به احتمال زیاد افزایش آلاینده های ازون و ترکیبات گوگردی عامل اصلی بروز بیماری های تنفسی است زیرا نتیجه تحقیقات نشان می دهد وجود این آلاینده ها در افرادی که زمینه تنگی نفس دارند ، موجب حملات آسمی می شود.
وی خاطرنشان کرد: در سفری که حدود 2 هفته پیش به استان خوزستان داشتم شبکه ای از ایستگاه های سنجش آلودگی هوا شامل 15 ایستگاه در کل استان خوزستان و 4 ایستگاه در شهر اهواز راه اندازی شد.
ابتکار اظهارداشت:براساس اطلاعات به دست آمده از این ایستگاه ها گازهای ازون و گوگردی در این مدت در اهواز افزایش نیافته است بنابراین یا دستگاه های موجود در ایستگاه های سنجش آلودگی هوا مشکل دارند و یا این که یک آلاینده ناشناخته دیگری عامل بروز تنگی نفس در مردم شده است .
وی افزود : در اجلاس بین المللی آب و هوا مذاکرات زیادی با مسوولان کشورهای مختلف در منطقه برای کاهش میزان گرد و غبار انجام شد. همچنین از سازمان های بین المللی برای رسیدگی به وضعیت آلودگی شهر اهواز و چهار شهر غربی کشور که تحت تاثیر شدید پدیده ریزگردها هستند، قول مساعد گرفته شد.
ابتکار افزود : در دیدار با وزیر نفت کشورمان در مورد ارتقای استاندارد سوخت به سوخت یورو 4 مذاکراتی انجام شد و در این دیدار وزیر نفت قول داد با وجود تمام محدودیتی های موجود و به رغم تحریم ها که نقش عمده ای در نرسیدن به استاندارد یورو 4 داشته اند، اقدام لازم برای ارتقای استانداردهای سوخت انجام شود.
وی ابرازامیدواری کرد که خودروسازان به تعهدات خود در زمینه تولیدمحصول با استاندارد یورو 4 عمل کنند و خود را با سوخت یورو 4 هماهنگ کنند.
معاون رییس جمهوری گفت: خودرو سازان تاکنون چندین بار مهلت خود برای تولید خودور با استاندارد یورو 4 تمدید کردند اما باید این فرصت ها بازنگری شود که این امر در دستور کار سازمان محیط زیست قرار دارد.
وی تحریم ها را در کنار عوامل دیگر یکی دیگر از موانع وزارت نفت و وزارت صنعت ، معدن و تجارت برای ارایه سوخت و خودرو با استاندارد یورو 4 اعلام کرد و افزود: در اجلاس بین المللی تغییرات آب و هوا در ورشو از سران کشورها و سازمان ملل خواستیم که این تحریم های غیرقانونی را لغو کنند چرا که نقش عمده ای در تغییرات آب و هوایی دارد.
معاون رییس جمهوری یاداور شد : بنزین یورو 4 و گاز طبیعی بهترین نوع سوختی هستند که می توان از آنها استفاده کرد .سازمان بهداشت جهانی در گزارش اخیر خود اعلام کرد گازوییل در بهترین شرایط باز هم ذرات دوده ای تولید می کند که می تواند سرطان زا باشد در حالی که این شرایط برای بنزین یورو4 و گاز طبیعی صادق نیست.
وی در مورد موضع سازمان محیط زیست در اجرای طرح زوج و فرد سراسری خودروها تاکید کرد: سازمان محیط زیست به هیچ عنوان با دایمی شدن این طرح موافق نبود اما اگر سازمان هواشناسی به دستگاه هایی مجهز شود که بتواند پیش بینی های دقیق تری ارایه دهد می توان از یکی دو روز پیش از انباشت آلاینده ها و چند روز پس از آن ، این طرح را اجرا کرد.
اجلاس بین المللی تغییرات آب و هوا از 20 آبان ماه امسال به مدت 12 روز در دو سطح کارشناسی و عالی در ورشو پایتخت لهستان برگزار شد.
علاوه بر رییس سازمان محیط زیست ، معاون علمی و فناوری رییس جمهوری به همراه نمایندگانی از وزارتخانه های نفت ، نیرو ، وزارت امور خارجه و دیگر کارشناسان از کشورمان در این اجلاس حضور داشتند.
AO منفى به نفع ماست يا AO مثبت ؟
پاسخ : بستگى دارد ساير نوسانات در چه موقعيتى باشند و بستگى داره در چه ماهى باشيم
كلى گويى در هواشناسى خطاست
MJO مكمل AO مى باشد
پس وضعيت MJO هست كه مشخص ميكنه AO مثبت به نفع ماست يا AO منفى
AO مسئوليت تاوه قطبى و پرفشارهاى شمالى را بر عهده دارد
يه مطلب ديگر اينكه نيمه اول آذر امسال دوره پيش از طوفان است .
پاسخ : بستگى دارد ساير نوسانات در چه موقعيتى باشند و بستگى داره در چه ماهى باشيم
كلى گويى در هواشناسى خطاست
MJO مكمل AO مى باشد
پس وضعيت MJO هست كه مشخص ميكنه AO مثبت به نفع ماست يا AO منفى
AO مسئوليت تاوه قطبى و پرفشارهاى شمالى را بر عهده دارد
يه مطلب ديگر اينكه نيمه اول آذر امسال دوره پيش از طوفان است .
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
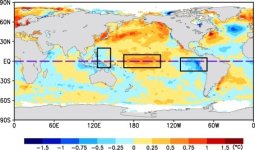
آخرین وضعیت انسو در ناحیه 3.4

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk
AO منفى به نفع ماست يا AO مثبت ؟
پاسخ : بستگى دارد ساير نوسانات در چه موقعيتى باشند و بستگى داره در چه ماهى باشيم
كلى گويى در هواشناسى خطاست
MJO مكمل AO مى باشد
پس وضعيت MJO هست كه مشخص ميكنه AO مثبت به نفع ماست يا AO منفى
AO مسئوليت تاوه قطبى و پرفشارهاى شمالى را بر عهده دارد
يه مطلب ديگر اينكه نيمه اول آذر امسال دوره پيش از طوفان است .
نه انصافا بسیار خوب هست انشا تون که باعت میشه اکثریت دوستان به راحتی مطلب درک کنن؛
شیمی جان قربان:خنده2::گل:
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
آخرین آپدیت cfs v2 از چشم انداز بارش روزهای پیشرو

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
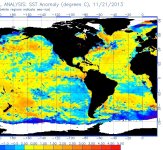
دمای آب در خلیج مکزیک به شدت افزایش پیدا کرده!
آیا طوفانهای پی در پی در روزهای پیشرو ایالات متحده را در هم خواهد کوبید؟

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk
آیا طوفانهای پی در پی در روزهای پیشرو ایالات متحده را در هم خواهد کوبید؟

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk
حالا ََََAOمنفی باشه امیر جان تاوه قطبی به عرضهای پایین تر نفوذ میکنه؟یا خیر اگر مثب باشه؟AO منفى به نفع ماست يا AO مثبت ؟
پاسخ : بستگى دارد ساير نوسانات در چه موقعيتى باشند و بستگى داره در چه ماهى باشيم
كلى گويى در هواشناسى خطاست
MJO مكمل AO مى باشد
پس وضعيت MJO هست كه مشخص ميكنه AO مثبت به نفع ماست يا AO منفى
AO مسئوليت تاوه قطبى و پرفشارهاى شمالى را بر عهده دارد
يه مطلب ديگر اينكه نيمه اول آذر امسال دوره پيش از طوفان است .
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
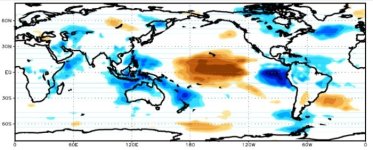
آنومالی دمای آب دریا ها ظرف 24 ساعت گذشته

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk

Sent from my SM-N900 using Tapatalk
اميدوارم بزودى امريكا شاهد يك طوفان قوى باشه
والله بستگى به وضعيت ساير نوسانات داره يه موقعى AO مثبت به نفع ماست يه موقعى هم AO منفى
در مورد دماى آبها : خليج پارس گرم باشه رطوبت زا ميشه يا وقتى سردتر از نرمال باشه ؟ پاسخ : وقتى خليج پارس گرم تر از نرمال باشه
در مورد خورشيد : وقتى لكه هاى خورشيد زياد ميشن بارشهاى ايران زياد ميشه يا وقتى خورشيد بدون لكه باشه ؟ پاسخ : وقتى لكه ها زياد باشه
والله بستگى به وضعيت ساير نوسانات داره يه موقعى AO مثبت به نفع ماست يه موقعى هم AO منفى
در مورد دماى آبها : خليج پارس گرم باشه رطوبت زا ميشه يا وقتى سردتر از نرمال باشه ؟ پاسخ : وقتى خليج پارس گرم تر از نرمال باشه
در مورد خورشيد : وقتى لكه هاى خورشيد زياد ميشن بارشهاى ايران زياد ميشه يا وقتى خورشيد بدون لكه باشه ؟ پاسخ : وقتى لكه ها زياد باشه
- وضعیت
- موضوع بسته شده است.