-
توجه: در صورتی که از کاربران قدیمی ایران انجمن هستید و امکان ورود به سایت را ندارید، میتوانید با آیدی altin_admin@ در تلگرام تماس حاصل نمایید.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
مباحث عمومی هواشناسی
- شروع کننده موضوع Amir Mohsen
- تاریخ شروع
- وضعیت
- موضوع بسته شده است.
سایت نروژ هم چه کرده برای فریدون شهر !!
دماها را داشته باشید با برفی که زده
http://www.yr.no/place/Iran/Esfahan/Fereydūnshahr/long.html
دماها را داشته باشید با برفی که زده
http://www.yr.no/place/Iran/Esfahan/Fereydūnshahr/long.html
Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
در ارتباط با سرمای پیشرو ، تصور بر این هست که سرمایی که قراره وارد ایران بشه اروپاییه ولی اینطور نیست!
این نقشه آنومالی زیر نشون میده که سرما از سمت سیبری به منطقه ما نفوذ میکنه و اصولا با این سرمایی که فعلا در شرق اروپا دیده میشه کاملا متفاوته!!!!!!

این نقشه آنومالی زیر نشون میده که سرما از سمت سیبری به منطقه ما نفوذ میکنه و اصولا با این سرمایی که فعلا در شرق اروپا دیده میشه کاملا متفاوته!!!!!!

Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
در واقع اون سرمای شدید و فراگیری که قرار هست کشور ما رو از 14 دسامبر به بعد در بربگیره نطفه اش در منطقه قطب شمال و در شمالی ترین نقطه روسیه بسته میشه و گرنه این هوای سرد روزهای قبل از 15 دسامبر آنچنان فراگیر نیست و فوقش بتونه خیلی زور بزنه نوار شمالی -غربی آذربایجانها رو خیلی سرد کنه!!
اینو ببینید تا منشاء ظهور هوای سرد رو کامل متوجه بشید اون هوای سرد رو شمال شرق آفریقا باقیمانده همون هوای سرد اروپایی روزهای قبل از 15 دسامبر هست که بصورت یک سردچال در اومده:

اینو ببینید تا منشاء ظهور هوای سرد رو کامل متوجه بشید اون هوای سرد رو شمال شرق آفریقا باقیمانده همون هوای سرد اروپایی روزهای قبل از 15 دسامبر هست که بصورت یک سردچال در اومده:

Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
در واقع در شرف وقوع یک stratosphereic warming هستیم:


ali.doosti
کاربر ويژه
دست شما درد نکنه امیر جان یه کم دیگه تلاش کنه برف میاداینهم تقدیم به علی دوستی عزیز:
دزفول:
مشاهده پیوست 47905
فکونم امسالم دمای منفی داریم پس...
ali.doosti
کاربر ويژه
نروژ و جی اف اس هم بارشمونو کم کردن...واقعا امسال در حقمون ظلم شده! به کی بگم آبادان بیشتر از ما باریده :|
شب دوستان عزیز بخیر...به امید فعال شدن سرخ :گل:
شب دوستان عزیز بخیر...به امید فعال شدن سرخ :گل:
ali.doosti
کاربر ويژه
راستی دم این اکیوودر گرم که می دونه چقدر به امید نیاز داریم :خنده1:
60 تایی واسمون پیش بینی کرده :خجالت2:
60 تایی واسمون پیش بینی کرده :خجالت2:
در واقع در شرف وقوع یک stratosphereic warming هستیم:

یه چیزهایی در مورد این پدیده خوندم. ولی چیزی رو که متوجه نمیشم اینه که اثرش چه جوریه. یعنی روی کدوم مناطق هست. کل نیمکره شمالی یا اینکه باعث سرد شدن ناگهانی یه منطقه خاص میشه؟
Stratospheric Phenomenon Is Bringing Frigid Cold to U.S
- Published: January 21st, 2013

 By Andrew Freedman
By Andrew Freedman Follow @afreedma
An unusual event playing out high in the atmosphere above the Arctic Circle is setting the stage for what could be weeks upon weeks of frigid cold across wide swaths of the U.S., having already helped to bring cold and snowy weather to parts of Europe.
 Forecast high temperatures on Monday, Jan. 21, from the GFS computer model.
Forecast high temperatures on Monday, Jan. 21, from the GFS computer model.Click to enlarge the image. Credit: Weatherbell
This phenomenon, known as a “sudden stratospheric warming event,” started on Jan. 6, but is something that is just beginning to have an effect on weather patterns across North America and Europe.
While the physics behind sudden stratospheric warming events are complicated, their implications are not: such events are often harbingers of colder weather in North America and Eurasia. The ongoing event favors colder and possibly stormier weather for as long as four to eight weeks after the event, meaning that after a mild start to the winter, the rest of this month and February could bring the coldest weather of the winter season to parts of the U.S., along with a heightened chance of snow.
Sudden stratospheric warming events take place in about half of all Northern Hemisphere winters, and they have been occurring with increasing frequency during the past decade, possibly related to the loss of Arctic sea ice due to global warming. Arctic sea ice declined to its smallest extent on record in September 2012.
An Arctic cold front was sliding south from Canada on Friday, getting ready to clear customs at the border on Saturday and Sunday, bringing an icy chill to areas from the Plains states through the Mid-Atlantic by early next week, including what promises to be a chilly second inauguration for President Obama. Temperatures in Washington on Monday are expected to hover in the low 30s, only a touch milder than Obama’s first inauguration, when the temperature was 28°F.
Reinforcing shots of cold air are likely to affect the Upper Midwest, Great Plains and into the East throughout February, with some milder periods sandwiched in between.
Sudden stratospheric warming events occur when large atmospheric waves, known as Rossby waves, extend beyond the troposphere where most weather occurs, and into the stratosphere. This vertical transport of energy can set a complex process into motion that leads to the breakdown of the high altitude cold low pressure area that typically spins above the North Pole during the winter, which is known as the polar vortex.
The polar vortex plays a major role in determining how much Arctic air spills southward toward the mid-latitudes. When there is a strong polar vortex, cold air tends to stay bottled up in the Arctic. However, when the vortex weakens or is disrupted, like a spinning top that suddenly starts wobbling, it can cause polar air masses to surge south, while the Arctic experiences milder-than-average temperatures.
During the ongoing stratospheric warming event, the polar vortex split in two, allowing polar air to spill out from the Arctic, as if a refrigerator door were suddenly opened.

When the sudden stratospheric warming event began in early January, that signaled to weather forecasters that a cool down was more likely to occur by the end of the month, since it usually takes many days for developments in the stratosphere to affect weather in the troposphere, and vice versa.
“For reasons I don’t think we fully understand, the changes in the circulation that happen in the stratosphere [can] descend down all the way to the Earth’s surface,” said Judah Cohen, director of seasonal forecasting at Atmospheric and Environmental Research (AER) in Massachusetts.
As the polar stratosphere warms, high pressure builds over the Arctic, causing the polar jet stream to weaken. At the same time, the midlatitude jet stream strengthens, while also becoming wavier, with deeper troughs and ridges corresponding to more intense storms and high pressure areas. In fact, sudden stratospheric warming events even make so-called “blocked” weather patterns more likely to occur, which tilts the odds in favor of the development of winter storms in the U.S. and Europe.
Cohen was the lead author of a 2009 study that found that sudden stratospheric warming events are becoming more frequent, a trend that may be related to an increase in fall snow cover across Eurasia. The increase in snow cover has in turn been tied to the rapid loss of Arctic sea ice, since the increase in open water in the fall means that there is more atmospheric moisture available to fall as rain or snow.
Cohen and his colleagues at AER have been using an index of Eurasian snow cover during the month of October in order to make seasonal weather forecasts for the following winter, and he said that by using this technique, they successfully predicted the ongoing stratospheric warming event 30-days in advance.
“As far as I know this is a first and has huge implications for intraseasonal predictions,” he said.
 Computer model forecast for February, showing widespread cooler than average conditions in much of the U.S.
Computer model forecast for February, showing widespread cooler than average conditions in much of the U.S.Click to enlarge the image. Credit: Weatherbell.
Cohen’s research has also pointed to stratospheric warming events as one of the reasons why the second half of recent winters in the Northern Hemisphere have turned out to be colder than the first half.
“Scientists about a decade ago predicted that stratospheric warmings would become less frequent with climate change, however, just the opposite has happened and they have become more frequent. There is a positive trend in stratospheric warmings since the turn of the century and I have argued this is contributing to more severe winters,” he said.
When the vortex becomes dislodged from the pole, Cohen said, it can lead to a flow of air that is more north to south than west to east. “So when the warm air rushes the pole it displaces the cold air over the pole and forces it equatorward,” Cohen said.
This has major implications for U.S. winter weather.
High temperatures in North Dakota and Minnesota may not make it above zero Fahrenheit on Sunday and Monday. If Minneapolis records a high temperature below zero it will end its record-breaking streak of four years without such an occurrence. By Tuesday, the cold air will have spilled into Kentucky and Maryland as well as New England. And the long-range outlooks suggest that February is going to be a colder-than-average month from the Upper Midwest to the East Coast, although there may be brief breaks from the cold depending on the prevailing storm track.
Anthony Artusa, a seasonal climate forecaster at the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), said the cold air spilling southward for the inauguration may mark the beginning of a long-lasting cold period that is related to the stratospheric warming event. “It does look like this could be the early effects of it,” he said during a conference call with reporters on Thursday.
What is a Polar Stratospheric Warming?
A stratospheric sudden warming is perhaps one of the most radical changes of weather that is observed on our planet. Within the space of a week, North Pole temperatures can increase by more than 50 K (90°F). For example, on 17 January 2009 the temperature at the North Pole near 30 km was about 200 K. Over a 5-day period, the temperature increased to 260 K (a change of 60 K or 108°F).
These stratospheric sudden warmings are caused by atmospheric waves that originate in the troposphere. The waves are forced by the large-scale mountain systems of the northern hemisphere and the land-sea contrasts between the continents and oceans. The waves are also characterized by their very large scales, typically referred to as planetary-scale waves. The stratospheric wind structure filters the smaller scale waves, only allowing the planetary waves to propagate into the stratosphere. As the waves move upward into the stratosphere they have two effects: first they will often push the polar vortex away from the North Pole—bringing warmer midlatitude air poleward, and second, they produce a downward motion field that also warms the polar region.
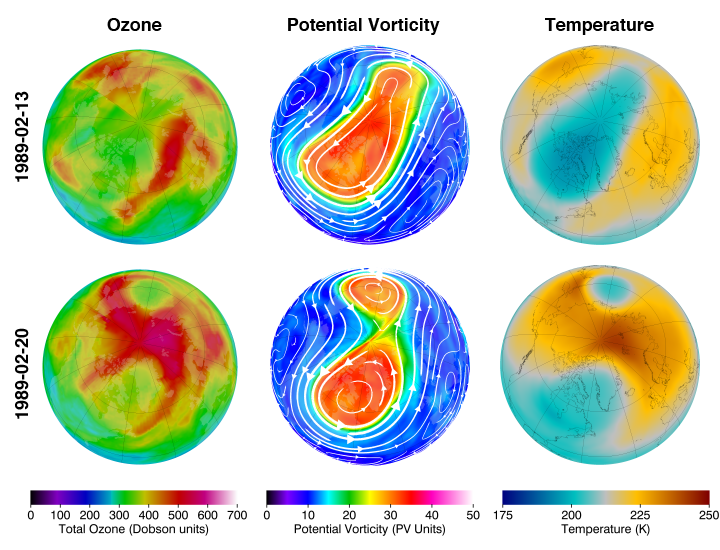
An example of a stratospheric warming is shown above. The top row of images are for 13 February 1989. The PV image indicates an elongated polar vortex (top middle image), while polar temperatures are relatively cold (top right) and total ozone is relatively low (top left). A week later on 20 February 1989, the polar vortex has split into two separate parts (bottom middle). This is known as a wave-2 pattern, since there are two high and two low centers. Note that the temperature (bottom right) and total column ozone (bottom left) have considerably increased at the pole. Other events are associated with a wave-1 pattern, where the vortex is displaced off the pole. This results in one side of the hemisphere having a relative high, while the other side has a relative low.
The most dramatic stratospheric sudden warmings are known as major warmings. During a major warming, at about 30 km the normal cold polar and warm midlatitude gradient is reversed and the west-to-east polar night jet reverses to an east-to-west flow. Sudden warmings are always characterized by large-scale, large-amplitude wave events. While major warmings only occur every other winter or so, wave events of weaker amplitude occur frequently during the winter season. All of these wave events act to warm and increase ozone levels in the polar region generally in proportion to their amplitude. The waves also act to strip off streamers of the polar vortex (similar to the cutting of a lathe). The waves cumulatively act to keep the polar region much warmer and ozone much higher during the winter than would occur in their absence.
The final warming is the last stratospheric warming of the season. After this warming, the stratosphere never recovers to its previous state and the vortex breaks up and dissipates. The final warming often occurs in March or April. Sometimes the stratosphere never recovers from what would otherwise be a mid-winter major warming in January or February, and that warming becomes the final warming.
آخرین ویرایش:
Lake-Effect (Enhanced) Snows
During the winter, when the weather in the Midwest is dominated by clear and cold polar
or arctic air, people living on the eastern shores of the Great Lakes brace themselves for heavy snow showers. Snowstorms that form on the downwind side of one of these lakes are known as lake-effect snows. Since the lakes are responsible for enhancing the amount of snow that falls on its downwind side, these snowstorms are also called lake-enhanced snows, especially when the snow accompanies a cold front or mid-latitude cyclone. These storms are highly localized, extending from just a few kilometers to more than 100 km inland. The snow usually falls as a heavy shower or squall in a concentrated zone. So centralized is the region of snowfall, that one part of a city may accumulate many inches of snow, while, in another part, the ground is bare. Lake-effect snows are most numerous from November to January. During these months, cold air moves over the lakes when they are relatively warm and not quite frozen. The contrast in temperature between water and air can be as much as 25°C (45°F). Studies show that the greater the contrast in temperature, the greater the potential for snow showers. In Fig. 1 we can see that, as the cold air moves over the warmer water, the air mass is quickly warmed from below, making it more buoyant and less stable. Rapidly, the air sweeps up moisture, soon becoming saturated. Out over the water, the vapor condenses into steam fog. As the air
continues to warm, it rises and forms billowing cumuliform clouds, which continue to grow as the air becomes more unstable. Eventually, these clouds produce heavy showers of snow, which make the lake seem like a snow factory. Once the air and clouds reach the downwind side of the lake, additional lifting is provided by low hills and the convergence of air as it slows down over the rougher terrain. In late winter, the frequency and intensity of lake-effect snows often taper off as the temperature contrast between water and air diminishes and larger portions of the lakes freeze.
Generally, the longer the stretch of water over which the air mass travels (the longer the fetch), the greater the amount of warmth and moisture derived from the lake, and the greater the potential for heavy snow showers. In fact, studies show that, for signifi cant snowfall to occur, the air must move across 80 km (50 mi) of open water. Consequently, forecasting lakeeffect snowfalls depends to a large degree on determining the trajectory of the air as it fl ows over the lake.
برفهای (افزایش برف) ناشی از تاثیر- دریاچهDuring the winter, when the weather in the Midwest is dominated by clear and cold polar
or arctic air, people living on the eastern shores of the Great Lakes brace themselves for heavy snow showers. Snowstorms that form on the downwind side of one of these lakes are known as lake-effect snows. Since the lakes are responsible for enhancing the amount of snow that falls on its downwind side, these snowstorms are also called lake-enhanced snows, especially when the snow accompanies a cold front or mid-latitude cyclone. These storms are highly localized, extending from just a few kilometers to more than 100 km inland. The snow usually falls as a heavy shower or squall in a concentrated zone. So centralized is the region of snowfall, that one part of a city may accumulate many inches of snow, while, in another part, the ground is bare. Lake-effect snows are most numerous from November to January. During these months, cold air moves over the lakes when they are relatively warm and not quite frozen. The contrast in temperature between water and air can be as much as 25°C (45°F). Studies show that the greater the contrast in temperature, the greater the potential for snow showers. In Fig. 1 we can see that, as the cold air moves over the warmer water, the air mass is quickly warmed from below, making it more buoyant and less stable. Rapidly, the air sweeps up moisture, soon becoming saturated. Out over the water, the vapor condenses into steam fog. As the air
continues to warm, it rises and forms billowing cumuliform clouds, which continue to grow as the air becomes more unstable. Eventually, these clouds produce heavy showers of snow, which make the lake seem like a snow factory. Once the air and clouds reach the downwind side of the lake, additional lifting is provided by low hills and the convergence of air as it slows down over the rougher terrain. In late winter, the frequency and intensity of lake-effect snows often taper off as the temperature contrast between water and air diminishes and larger portions of the lakes freeze.
Generally, the longer the stretch of water over which the air mass travels (the longer the fetch), the greater the amount of warmth and moisture derived from the lake, and the greater the potential for heavy snow showers. In fact, studies show that, for signifi cant snowfall to occur, the air must move across 80 km (50 mi) of open water. Consequently, forecasting lakeeffect snowfalls depends to a large degree on determining the trajectory of the air as it fl ows over the lake.
در طول زمستان وقتی هوای غرب میانه (ایالات متحده) تحت سیطرهی هوای سرد قطبی قرار میگیرد، مردم ساکن در سواحل شرقی دریاچههای بزرگ (Great Lakes) خود را برای رگبارهای برفی سنگین آماده میکنن. (همینجا اشاره کنم که مردم ساکن در سواحل جنوب غربی کاسپین هم همینطور! :شاد2::ذوق زده
برفهای ناشی از تاثیر دریاچه، اغلب از نوامبر تا ژانویه فراوانی بیشتری دارند. در طول این ماهها، هوای سرد بر روی دریاچه حرکت میکند در حالی که آب دریاچه نسبتا گرم است و هنوز کاملا یخ نزده است. اختلاف دمایی بین آب دریاچه و هوای سرد میتواند به بیش از 25 درجه سانتی گراد برسد. تحقیقات نشان میدهند که اختلاف دمایی بیشتر، پتانسیل رگبارهای سنگین برفی را بیشتر میکند. در شکل 1 میتوانیم مشاهده کنیم که هوای سرد بر روی آب گرمتر حرکت میکند، تودهی هوای سرد به سرعت از پایین گرم شده و این مساله آن را شناورتر و ناپایدارتر میکند. هوای سرد به سرعت رطوبت دریافت کرده و اشباع میشود. رطوبت فراوان، باعث میشود بخارها متراکم شده و مه تشکیل گردد. همچنان که هوا گرم میشود صعود کرده و ابرهای کومولوس شکل، تشکیل شده و هر چه هوا ناپایدارتر میگردد بر رشد این ابرها نیز افزوده میشود. در نهایت این ابرها باعث ریزش رگبارهای سنگین برفی میشوند و چنین به نظر میرسد که دریاچه همانند یک کارخانه برف سازی عمل میکند.
هنگامی که هوا و ابرها به مناطق در جهت وزش باد دریاچه میرسند، عمل صعود بیشتر بوسیله تپهها انجام گرفته و همگرایی هوا بر روی زمینهای ناهموار کاهش مییابد. در اواخر زمستان، در حالی که اختلاف دمایی بین آب دریاچه و تودههای هوای سرد کاهش مییابد و بخشهای وسیعی از دریاچه یخ میزند، فراوانی و شدت برفهای ناشی از تاثیر دریاچه اغلب به تدریج متوقف میشوند.
شکل 1: شکل گیری برف ناشی از تاثیر دریاچه. هوای سرد و خشک در حال عبور از روی دریاچه، از آب دریاچه رطوبت و گرما دریافت میکند. هوای شناور و ناپایدارتر صعود کرده و ابرهایی تشکیل میدهد که باعث ریزش حجم زیادی از برف در سواحل باد پناه (در مسیر جهت وزش باد) دریاچه میگردد.
به طور کلی، حرکت تودهی هوا سرد در مسیر طولانیتری از آب دریاچه (طی شدت مسافت بیشتر) باعث افزایش رطوبت و گرمای دریافت شده از دریاچه میگردد و پتانسیل ریزش سنگین رگبار برف را افزایش میدهد. در حقیقت، تحقیقات نشان می دهند که برای آنکه چنین ریزش برفی اتفاق افتد باید توده هوا حدود 80 کیلومتر بر روی آب دریاچه حرکت کند. بنابراین پیش بینی تاثیر دریاچه بر میزان بارش برف تا حد زیادی به تعیین مسیری که تودهی هوای سرد بر روی دریاچه میپیماید بستگی دارد.

Amir Mohsen
متخصص بخش هواشناسی
سلام دوستان عزیز
امروز آسمان مشهد در شرق و غرب کاملا متفاوت هست و بنظر میرسه سمت شهر با ابرهایی از جنس آلودگی ها و مه مواجه هستیم و این در حالی هست که در غرب مشهد ابرهای بسیار زیبا و امیدوار کننده ای از سامانه پیشرو به چشم میخوره!
امروز این ابرها رو که دیدم خیلی امیدوار شدم به فعالیت سامانه جدید:

خوب امروز تونستم یک دونه عکس از محدوده قله شیرو باد بگیرم که بنظر میرسه بینالود در روزهای گذشته برف خیلی خوبی دشت کرده:

امروز آسمان مشهد در شرق و غرب کاملا متفاوت هست و بنظر میرسه سمت شهر با ابرهایی از جنس آلودگی ها و مه مواجه هستیم و این در حالی هست که در غرب مشهد ابرهای بسیار زیبا و امیدوار کننده ای از سامانه پیشرو به چشم میخوره!
امروز این ابرها رو که دیدم خیلی امیدوار شدم به فعالیت سامانه جدید:

خوب امروز تونستم یک دونه عکس از محدوده قله شیرو باد بگیرم که بنظر میرسه بینالود در روزهای گذشته برف خیلی خوبی دشت کرده:

- وضعیت
- موضوع بسته شده است.









